Dive Into the Ocean: Exciting Dolphin Truths for Ocean Lovers
The globe of dolphins presents a remarkable crossway of knowledge, social behavior, and ecological relevance. From their intricate interaction methods to their outstanding analytical abilities, dolphins test our understanding of animal knowledge.
Dolphin Variety Diversity
Diversity is a trademark of the dolphin household, incorporating a large range of varieties that display unique physical features, habits, and environments. The household Delphinidae, commonly referred to as oceanic dolphins, consists of around 37 varieties, each adjusted to particular environmental niches. For instance, the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) is renowned for its intelligence and adaptability, prospering in both coastal and open sea settings.
In contrast, the whale (Orcinus orca), typically referred to as the awesome whale, is the biggest participant of the dolphin family members and is defined by its striking black-and-white pigmentation. Orcas demonstrate complex social frameworks and searching strategies, showcasing the behavioral variety within the household. Various other varieties, such as the rewriter dolphin (Stenella longirostris), are noted for their acrobatic display screens and preference for warmer waters, highlighting the flexibility of dolphins to various marine communities.
Additionally, river dolphins, including the pink river dolphin (Inia geoffrensis), inhabit freshwater atmospheres, additionally showing the extensive environments that dolphins occupy. Dolphin Facts. This unbelievable variety not just improves aquatic environments but likewise stresses the value of preservation initiatives to secure these exceptional creatures and their settings
Social Habits and Communication
The elaborate social habits and communication techniques of dolphins are crucial parts of their existence, promoting group communication and boosting survival. These extremely intelligent aquatic animals show complex social structures, commonly developing sheathings that can range from a couple of people to over a hundred. Within these groups, dolphins engage in behaviors such as cooperative hunting, social play, and mutual protection, which foster solid bonds amongst members.
Dolphins make use of an advanced selection of vocalizations, including clicks, whistles, and body movement, to convey information and express feelings. Their signature whistles act as one-of-a-kind identifiers, comparable to names, allowing individuals to call out to each other. This vocal interaction is complemented by non-verbal signals, such as jumping, slapping the water, and synchronized swimming, which better boosts their communications.
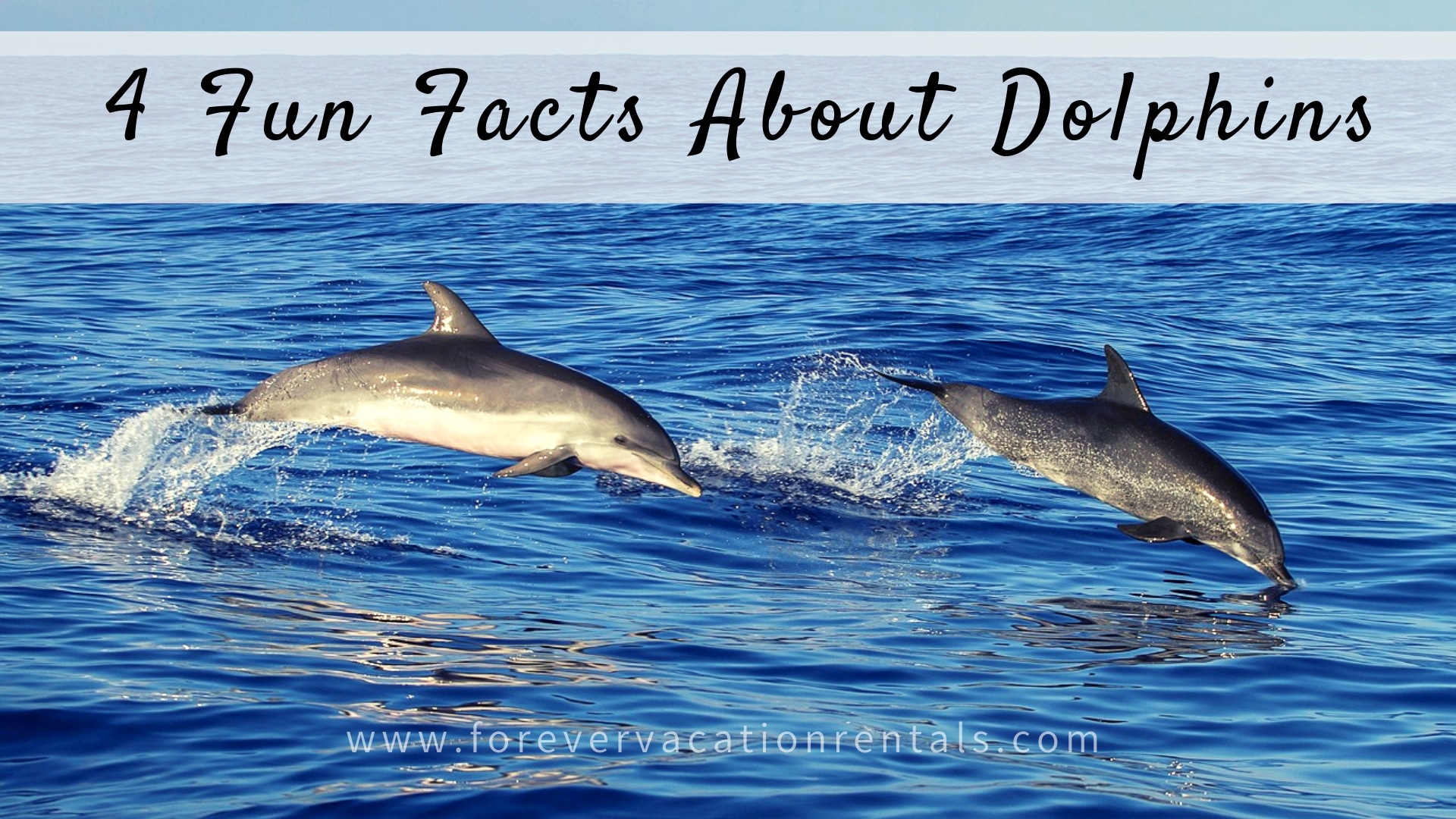
Unique Feeding Behaviors
Special feeding behaviors define dolphins, showcasing their flexibility and intelligence in different aquatic atmospheres. These marine creatures are recognized for their varied diets, which mostly include fish, squid, and crustaceans. Their searching strategies can differ dramatically, commonly customized to the particular prey and ecological problems.
One remarkable approach is cooperative hunting, where dolphins function in groups to herd colleges of fish into limited developments, making it simpler for individuals to capture their meal. This social habits not only boosts their feeding efficiency however likewise reinforces social bonds within the capsule. Furthermore, dolphins have been observed employing a method called "fish-whacking," where they use their tails to confuse or stun fish, facilitating much easier capture.
One more remarkable feeding routine is echolocation, which allows dolphins browse around this web-site to find prey even in dirty waters. By sending out acoustic waves and analyzing the returning echoes, they can determine the size, form, and location of their targets. This impressive capability emphasizes their adaptability in various habitats, from shallow seaside areas to deeper oceanic waters. Generally, the special feeding habits of dolphins highlight their function as proficient predators within the aquatic environment, demonstrating both knowledge and ingenuity.
Intelligence and Problem Addressing
Their intelligence is evident in their analytic skills, social interactions, and ability for learning. Study has demonstrated that dolphins can use tools, such as using aquatic sponges to secure their rostrums while foraging on the seafloor.
Additionally, dolphins display advanced interaction skills, employing an intricate system of clicks, whistles, and body movement. Dolphin Facts. This interaction is critical for coordinating group tasks, such as hunting and interacting socially, highlighting their capability to work jointly in the direction of an usual goal. Their capacity to recognize abstract principles, consisting of self-recognition in mirrors, better stresses their cognitive sophistication
In regulated researches, dolphins have shown a capability to fix problems and execute tasks that call for both memory and important thinking. These interactions show not just knowledge yet likewise a determination to involve with their environment in novel means. In general, the cognitive expertise of dolphins positions them among one of the most smart types on earth, fostering a much deeper admiration for their function in aquatic ecosystems.
Conservation and Environmental Effect
Conservation initiatives targeted my review here at safeguarding marine ecosystems are critical for preserving dolphin populaces and their environments. Dolphins are very conscious ecological changes, and their survival is intricately connected to the wellness of nautical ecological communities. Overfishing, contamination, and climate modification posture significant threats to both dolphins and their settings.
Overfishing interrupts the food web, causing a decrease in target types essential for dolphin survival. Toxins such as plastics and chemicals collect in aquatic environments, endangering dolphins via consumption and bioaccumulation. Raised water temperature levels and sea acidification, effects of environment modification, even more jeopardize the delicate equilibrium of aquatic ecological communities, influencing dolphin breeding and migratory patterns.
Conservation initiatives, consisting of the facility of marine protected locations (MPAs), play an essential duty in securing these intelligent creatures. MPAs aid minimize human effect, allowing ecosystems to recoup and prosper. Public recognition projects and community involvement are likewise necessary, fostering a society of stewardship in the direction of marine life. By focusing More hints on conservation initiatives, we can make sure that future generations delight in the elegance and vigor of dolphins and the oceans they populate. Safeguarding aquatic environments is not almost saving dolphins; it has to do with protecting the intricate internet of life that maintains us all.
Final Thought
Dolphins exhibit the complexity and splendor of marine life via their diverse species, complex social structures, and progressed cognitive abilities. Their distinct feeding behaviors and communication approaches even more show their flexibility and intelligence. As crucial parts of marine environments, dolphins emphasize the necessity of ongoing conservation initiatives to guard their habitats. Safeguarding these exceptional animals is vital not just for their survival yet also for maintaining the health and balance of ocean atmospheres around the world.
Various other types, such as the spinner dolphin (Stenella longirostris), are noted for their acrobatic screens and preference for warmer waters, highlighting the versatility of dolphins to numerous aquatic ecological communities.
On the whole, the one-of-a-kind feeding behaviors of dolphins highlight their duty as experienced predators within the aquatic ecological community, showing both knowledge and resourcefulness.
In general, the cognitive prowess of dolphins places them among the most smart types on the world, fostering a much deeper admiration for their function in marine ecosystems.
